Our Services
What We Offer
Our E-Learning platform offers flexible workforce solutions for you and your employees. Our services cater to both individuals and corporations.

About us
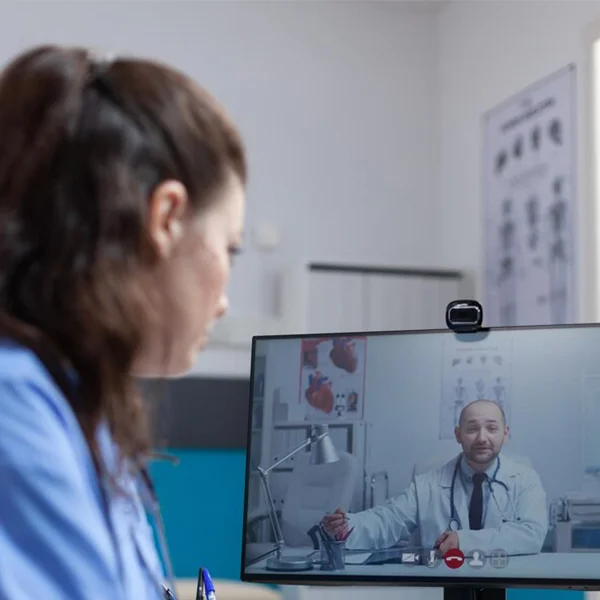
E-Learning for Compliance, Growth, and Safety Program
W
e go beyond compliance training. Our E-Learning platform supports employee growth,
safety, and well-being. We offer many courses. They enable healthcare professionals
to excel in their roles. They ensure a safe, productive work environment.
Build compliance, growth, and
wellness together!
Customizable E-Learning Solution
Protect & Educate with E-Learning Solutions

01
Compliance Awareness
Reduce the risk of costly fines and penalties.

02
Improve Service
Deliver exceptional care to your patients.

03
Lower Risks
Reduce potential liabilities and protect your organization.

04
Educate Employees
Ensure everyone is on the same page and fully informed.
Custom Compliance Training
Workforce Solutions Modified With Your Needs
*Our team of experts will work closely with you to develop training that's:
Relevant: Custom training solutions for your specific profession and needs.
Engaging: Interactive and impactful.
Effective: Proven to drive results.
Reject cookie-cutter training. Partner with American Healthcare Compliance today and discover the difference. Set to advance your organization to the next level?


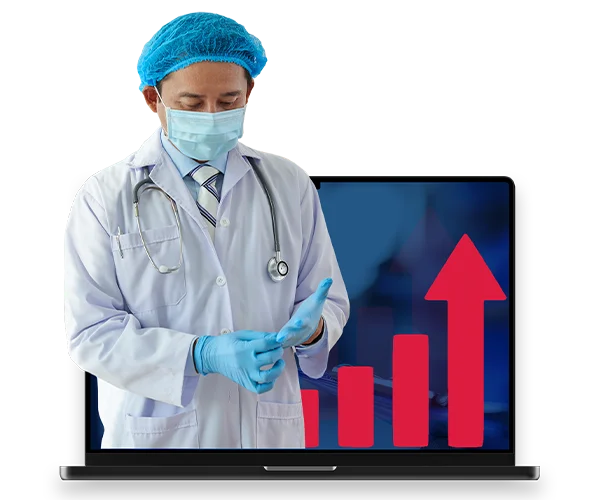
Monitor Your Team's Performance
Our platform provides instant data to track progress, certifications, and healthcare training programs. It helps you make better decisions and improve performance.
Compliant Solutions
We Work For
We proudly work for organizations of all sizes. This includes small clinics and large healthcare networks. Our compliance training works for:

Doctors, Nurses & Healthcare Providers
Staying updated on industry regulations.
Dental Clinics & Orthodontists
Maintaining best practices in patient care and safety.


Hospitals & Medical Centers
Committed to high standards of compliance.

Pharmacies & Laboratories
Requiring strict compliance to healthcare laws.

Accessible Learning
Your Compliance, Your Schedule
W e know healthcare providers are always on the move. That's why our online compliance training is designed to fit your busy lifestyle.
Start, Stop, Continue: You can start, stop, and restart courses whenever you want. Learn at your speed and schedule. This flexibility lets you balance education with life's demands.
Learn at Your Pace: Study at your pace. Fully understand each module. Take time with the lessons. Avoid rushing. Aim for steady progress and deep understanding.
Mobile-Optimized: Learn anywhere, anytime with our mobile platform. Simply use your phone or tablet to access knowledge.
What Our Clients Say!
At American Healthcare Compliance, we proudly offer high-quality E-Learning solutions. These solutions help healthcare organizations. They stay compliant, increase safety at work, and support employee growth. Here’s what our clients have to say about their experience with us.

Compliance Made Simple – Learn, Track, and Grow.
American Healthcare Compliance: We assist healthcare employees with e-learning, managing training, and tracking progress in real time. This creates a smarter and safer workplace.